The number of chlorides replaced depends on the ratio of reactants.
Converting silicon metal to methylchlorosilane can be done using chloromethane and a bit of copper. This is called the Rochow process:
n can take the value of 1 - 3.
Chloromethane can then be hydrolysed to trimethylsilanol:
Which condenses to a dimer:
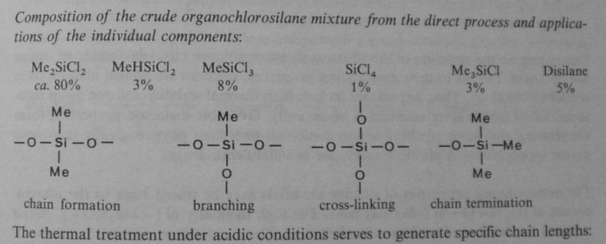
With Me2SiCl2, this forms chains or rings called silicones - molecules with a Si-O-Si backbone. The Si-O bond is much stronger than Si-Si, and is similar in strength to a C-C bond, so it allows very long chains.
Larger numbers of chlorides, when hydrolysed, produce branching and cross-linking:
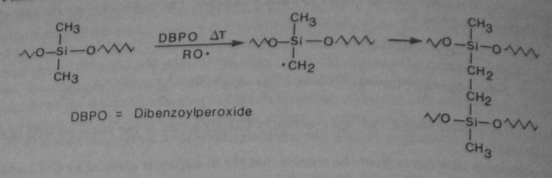
Branching between methyl groups can also be achieved. This is done by using Benzoyl Peroxide, a radical initiator:
Liquid silicones are more stable than hydrocarbons, and have a much lower change of viscosity with temperature. Thus they are used in brake fluid.
Silicones are hydrophobic, so they are used in water-proof sprays for shoes.
Low-mass silicones are used in shampoo, conditioner, shaving foam, hair gel, and toothpaste, to impart a silky feel.
Larger-mass greases, oils and resins are used for sealants, lubricants, varnishes, and synthetic rubbers

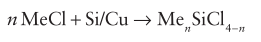
No comments:
Post a Comment