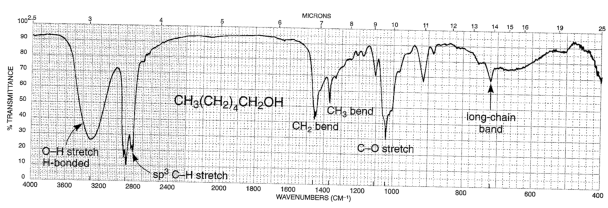
O-H stretch: The free O-H stretch is a small sharp peak at 3650-3600.
The hydrogen-bonded O-H stretch is a broad strong peak at 3400-3300.
For the neat liquid, all the alcohol is considered hydrogen bonding, so the broad peak is the only one of the two visible. As the alcohol is dissolved in a non-hydrogen bonding solvent, the free O-H peak becomes more visible:
The right-side picture is of an extremely diluted alcohol, or a gas.
C-O-H bend: Broad weak peak at 1440-1220, often obscured by CH3 bends.
C-O: Stretch occurs at 1260-1000
1-Hexanol:
2-Butanol:
Para-cresol:
The free O-H stretch occurs near 3640, 3630, 3620, 3610 for primary, secondary, tertiary, and phenolic alcohols respectively. But resolving frequency differences this small requires careful calibration, so these distinctions are of no use.
Intramolecular hydrogen bonding usually shifts the O-H stretch to a lower frequency. For example, for methyl silicate it is situated about 3200, around 150 less then the average phenol.
The strong C-O stretch at 1260-1000 can be used to determine the structure of the alcohol, notably more easy than with the O-H stretch:
.pdf+-+SumatraPDF_2012-12-09_00-18-51.png)
.pdf+-+SumatraPDF_2012-12-09_00-32-42.png)
.pdf+-+SumatraPDF_2012-12-09_00-33-20.png)
.pdf+-+SumatraPDF_2012-12-09_00-34-04.png)
.pdf+-+SumatraPDF_2012-12-09_01-00-10.png)
Can you please help outline the differences between free and bonded OH ? Im struggling to understand this bit please?
ReplyDeletebonded oh means interaction of oh with the environment which makes the peak broad and intense but round at the bottom.
DeleteWhat is the difference between free O-H bond and bonded O-H
DeleteHydrogen bonded alcohols (H...OH- or H on O, N or F) show lower frequency than free or non bonded alcohols OH groups.
ReplyDeleteTamil PArent
nice
ReplyDeleteBOC Sciences provides a wide range of research chemicals and biochemicals including inhibitors, building blocks, GMP Products, impurities and metabolites, APIs for Veterinary, Natural Compounds, ADCs, Stem Cell Molecule and chiral compounds. Moracin P
ReplyDeleteTHANKS
ReplyDeleteCan u describe the weak peak unless conjugated in IR spectrogram
ReplyDelete*breaks down door* hey it's me goku
ReplyDeleteso no cock and ball torture?
ReplyDeleteOur complete suite of CRO services spans the entire molecule development pipeline including contract research for target identification, building blocks, compound synthesis, biochemical and cellular analysis, preclinical animal tests, and clinical studies. 2,4,7-Trihydroxy-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene
ReplyDeleteWhy are phenols c-o of a higher wavenumber than alcohols?
ReplyDeleteBecause unlike the alcohols, the C-O bond in phenols have double bond character, due to conjugation. Since the bond order slightly increases because of this, the bond becomes stronger, the spring force constant increases, and the vibrational frequency (wavenumber) also increases!
Delete